The Essential Digits of Pi: How Many Do We Really Need?
Written on
Understanding the Significance of Pi
Pi, represented as 3.14159265358979323846..., is a mathematical constant that defines the ratio of a circle's circumference to its diameter. Recognized as an irrational number, Pi cannot be accurately depicted through simple fractions. Its history dates back to the ancient Greek mathematician Archimedes, who estimated its value between 3.1408 and 3.4129 around 250 B.C. Fast forward to 2021, and mathematicians have calculated Pi to over 50 trillion digits beyond the decimal point, with no end in sight.
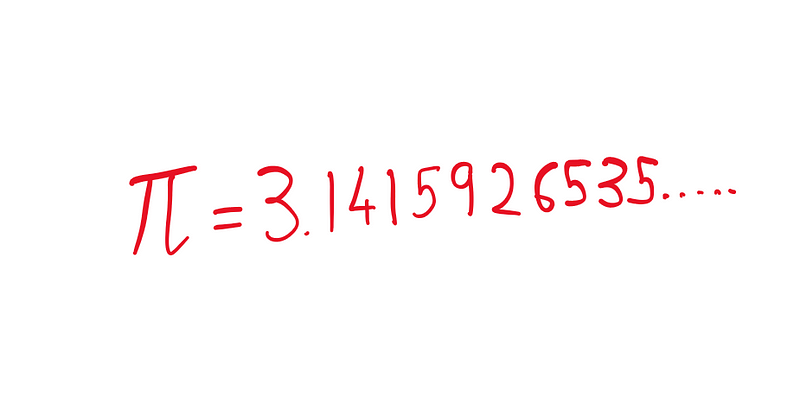
However, this leads to an important question: How many digits of Pi are truly necessary in real-world applications? Is calculating Pi to 50 trillion digits really warranted? In this article, we will explore these questions through practical examples and discuss the industry standards regarding Pi.
What Precision Do Calculators Use?
During my time as an engineer, I frequently relied on scientific calculators, which offer more advanced functionalities than standard calculators. My personal calculator, the CASIO fx-991ES PLUS, is equipped with Pi as a default constant, using only the first 9 digits after the decimal point. This brings us to an interesting inquiry: Do engineers really need more than 9 digits of Pi? Let's find out.
Using Pi in Practical Scenarios
For instance, if we wish to compute the circumference of a circle with a diameter of 1 kilometer (Km), we can examine two approximations of Pi:
- Pi_Short = 3.141593 (6 digits after the decimal)
- Pi_Long = 3.141592653589793 (15 digits after the decimal)
Using the formula for circumference (C = pi times D) (where (D) is the diameter), we can calculate:

For a circle with a 1Km diameter, the difference in accuracy between the two Pi approximations is less than 0.04 cm. What if we utilize a more precise version of Pi? Let's explore:
- Pi_Super_Long = 3.1415926535897932384626433 (25 digits after the decimal)
Calculating the circumference with this version, we find:
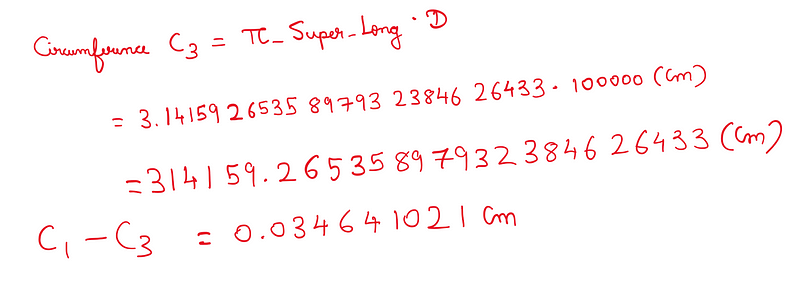
The additional accuracy gained when transitioning from Pi_Long to Pi_Super_Long is merely 0.000001021 cm. In practical terms, when dealing with a circle of 1Km in diameter, an error margin of around 1 cm is typically acceptable. Thus, it's safe to conclude that 6 decimal places of Pi suffice for most applications.
Industry Standards for Pi Usage
In sectors where precision is crucial, such as aerospace, the need for accuracy is paramount. For instance, NASA employs the first 15 digits of Pi when designing systems for projects that reach up to 125 billion kilometers in diameter, which results in an error margin of approximately 3.81 cm.
On another front, the motorsport industry, specifically Formula 1, utilizes only the first four digits of Pi, demonstrating that even high-performance vehicles operate effectively with a minimal number of digits.
Why Do We Calculate Pi to Over 50 Trillion Digits?
Given that organizations like NASA and Formula 1 operate successfully with just a few digits, why do researchers pursue calculations extending to trillions of digits? The answer lies in humanity's fascination with Pi as a mathematical constant. The endeavor to compute additional digits often serves as a platform to test new algorithms and supercomputer capabilities, rather than a necessity for practical applications.
In conclusion, while the exploration of Pi's digits is intellectually stimulating, for most real-world uses, the first 15 digits are more than adequate. I hope you found this discussion insightful. If you enjoyed this article, consider showing your support by liking, following, or subscribing.
Further Reading Recommendations
If you're interested in exploring more mathematical concepts, you might enjoy: "Why Is 3 A Special Denominator In Division?" and "What Exactly Is Zero Raised To The Power Zero?"
In the video titled "How Many Digits of Pi Do We Really Need?", we delve deeper into the practical implications of Pi's digits in various fields.
Another insightful video, "How many digits of pi (𝜋) do we really need?", further explores the necessity of Pi's precision in everyday calculations.